
Products
We manufacture plate materials by rolling Mg alloy and supply them to various demand industries.
About Mg
Pure Mg
Atomic number 12, Atomic weight 24.3
HCP(Hexagonal Cross Packed) structure lattice
Infinite resource
- Abundant element (8th in earth crust, 3rd in sea water)
- Extracted from mineral ore and sea water (electrolytic method and thermal reduction method)
The lightest element among the structural metal elements
Increase of strength and elongation by alloying pure Mg with other elements
Mg Alloy

Suitable for designing lightweight parts due to high specific strength
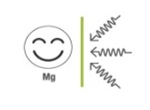
Good for vibration absorbency due to high vibration loss coefficient
(Vibration loss coefficient: Mg 1.48 vs. Al 0.88)
Superior machinability due to lower machining power requirement (80% of Al)
Suitable for application on 3C products due to high electromagnetic wave shielding
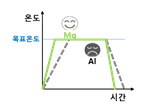
Suitable for rapid heating and cooling due to low thermal capacity
Easy to recycle, similar to steel and Aluminum
Material Comparisons
| Material | Mg Alloy | Steel | AI Alloy | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AZ31B | E-form | Heat Sinker | GA | STS304 | 5052-H32 | 6061-T6 | |
| Density (g/㎤) | 1.78 | 1.80 | 1.74 | 7.87 | 8.0 | 2.66 | 2.69 |
| Modulus of Elasticity (GPa) | 45 | 45 | 45 | 201 | 200 | 70 | 69 |
| Tensile Strength(MPa) | 260 | 255 | 220 | 320 | 505 | 290 | 310 |
| Yield Strength(MPa) | 180 | 150 | 155 | 200 | 215 | 193 | 276 |
| Elongation (%) | 17 | 25 | 14 | 28 | 40 | 22 | 12 |
| Thermal Conduct. (W/m·K) | 85 | 110 | 138 | 46 | 16 | 138 | 167 |
| Specific Heat (J/gk) | 1.033 | 0.994 | 1.023 | 0.47 | 0.5 | 0.963 | 0.908 |
| Electric Conduct.(x10-5 Ω·cm) | 0.92 | - | - | 1.42 | 7.20 | 0.50 | 0.40 |
| Machinability (%) | 100 | 100 | - | 55 | - | 30 | - |
| Melting Point (°C) | 632 | 800 | 650 | 1.515 | 1.455 | 638 | 646 |
